Denis Petros, “General Nursing: Challenging, Yet Rewarding”
General nurses are individuals who provide direct care for their patients such as bathing and dressing them, giving prescribed medication, and collecting fluid samples. The requirements to become a general nurse are rigorous. They have to obtain a bachelor’s degree in nursing, pass the National Council Licensing Examination (NCLEX), and pass a background check. In addition, nurses have to be prepared mentally to face any sort of challenging and scary experiences throughout their career. They put their lives on the line in order to help patients to the best of their abilities. The nursing profession is full of obstacles like becoming mentally exhausted and developing a lot of stress, but these can be overcome with thriving motivation, empathy, and an ability to consult with patients.
In order to grasp the scope of what general nurses do, it’s important to understand what their workday looks like. Nurses usually work eight to twelve hours a day with barely any breaks. Those who work in hospitals usually have to take care of many patients on a daily basis. In addition to the work overload and the countless hours they have to spend taking care of patients, nurses also have to deal with environmental stressors. As Jasmina Starc mentions in “Stress Factors among Nurses at the Primary and Secondary Level of Public Sector Health Care: The Case of Slovenia,” “[R]esearch shows that nurses experience stress due to: a lack of staff and the resulting excessive workload, highly demanding work and tasks, too high expectations from and inappropriate attitudes of superiors, poor work organization, and not getting along with co-workers.” Nursing is a type of occupation that mostly consists of communication with fellow nurses, the ability of working together, and the ability to overcome challenges. The lack of communication and teamwork is a major cause of stress among nurses. This is due to the fact that a lot of nurses have a lot going on with their patients and the tasks they are supposed to overcome, and they start feeling burnt out, which causes a lack of communication with other nurses. Duquesne University discloses, “Nurses are also required to work seamlessly with doctors and other nurses. Communication problems and personality clashes are inevitable and can lead to stress and frustration.” In order to accomplish multiple tasks at a rapid speed, nurses need to communicate with each other and give each other information on the tasks they are supposed to do in order to accomplish at the highest standard with few mistakes. However, this becomes extremely challenging because each nurse has their duty to serve, and with the added pressure from supervisors, patients, and the feeling of mental exhaustion, communication amongst a group of nurses starts to break apart, leading to disagreements and arguments that results into more high levels of stress.
This causes nurses to experience what is called “Nurse Burnout.” As defined by the University of St. Augustine, “Nurse burnout is the state of mental, physical, and emotional exhaustion caused by sustained work-related stressors such as long hours, the pressure of quick decision-making, and the strain of caring for patients who may have poor outcomes.” Nurse burnout is one of the main reasons nurses quit their jobs.
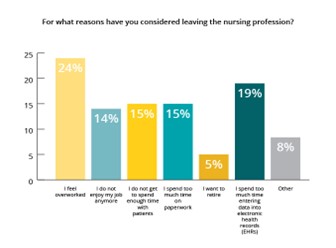
Graph 1
Fig.1, Cornwall, Liz, et al. “2018 Modern Nurse Survey: Nursing Shortage Leading to Nurse Burnout.” RNnetwork, 12 Dec. 2018, https://rnnetwork.com/blog/rnnetwork-2018-portrait-of-a-modern-nurse-survey/.
Nurse burnout has been increasing due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The reason behind it is the fact that nurses see a lot of their patients lose their lives to the virus and they start to feel a lot more stressed and exhausted. Nurses also fear that they might contract COVID-19 and spread it to their loved ones. According to Jeff Lagasse, in his article “Healthcare Workers Experiencing Burnout, Stress Due to Covid-19 Pandemic,” “More than three-quarters of healthcare workers with children said they were worried about exposing their child to COVID-19, nearly half were worried about exposing their spouse or partner, and 47% were worried that they would expose their older adult family members.” On top of feeling overwhelmed because of the tasks nurses have to do in order to take care of their patients, the stress and anxiety of infecting a loved one damages their mental and emotional health. The nursing career is extremely demanding on a person’s mental health, and their ability to cope with the challenges; however, once the solution to the problems are found, nursing becomes one of the most opportunistic careers to be in since it brings out the best in a person.
Motivation is the foundation of a nurse’s career. There are several types of motivation that nurses have: intrinsic motivation, integrated motivation, and identified motivation. Intrinsic motivation is the motivation in order to complete activities that require a lot of attention like a project of some sort. Maura Galletta, et al explain, “A nurse who is intrinsically motivated has a spontaneous interest in his/her work and hence expresses the highest degree of autonomous motivation.” By having intrinsic motivation, nurses are able to tackle challenges with the mindset of succeeding and finishing the task rather than thinking of failure. This increases their chances of completing tasks effectively and efficiently. Intrinsic motivation is the key factor that makes nurses passionate about supporting their patients, making them the number one priority and performing to the best of their abilities in order to provide the best care. Integrated motivation, or when activity of some sort triggers a set of values that are accepted by an individual, is another common form of motivation among nurses. This is most common because nurses will do activities based on the values that they follow. This mindset is mostly applied when nurses are taking care of patients because nurses value the care and support they give to their patients, which increases the chances of the patient recovering faster. It also changes the patient’s mindset since it gives them the idea that nurses are there to help and consult them rather than give them an uncomfortable feeling of visiting the hospital. The third key type of motivation nurses exhibit is identified motivation which arises out of conscious valuation of an activity. Nurses with identified motivation have the mentality that certain activities such as delivering patient information or filing certain documentation are essential to their line of work. Galletta, et al explain: “[N]urses sometimes perform activities that are not interesting per se (e.g., attending meetings, completing administrative work), but such activities can generate satisfaction because the nurses recognize that they are an essential part of the nursing process.” These activities are not as exciting as taking care of a patient, but they are big essentials that make nursing an important occupation. Nurses that have identified motivation tend to be more focused since the importance of doing a task such as filing patient documents gives the nurses the ability to perform timely and efficiently. With the help of motivation, nurses are able to bring out a new skill that they possess.
Nurses are often motivated to enter this field because of empathy. This job gives them the ability to consult with their patients and make them feel more comfortable. Nurses will do anything in their power, including providing comfortable clothing, in order to make the patient feel at home and forget about the uncomfortable visit to the hospital. Clark explains, “By going the extra mile to provide small comforts … patients don’t focus as much on the uncomfortable parts of their visit. They’ll be appreciative that … staff want to make their experience the best it can be despite medical reasons out of anyone’s control.” Nurses use empathy in their practice of comforting patients. This helps the nurses be more understanding of the patient’s situation, which leads to patient comfort. As discussed by Norwich University, “When receiving empathetic care, patients exhibit less anxiousness, improved self-concept, and lower levels of depression and hostility. Empathetic nurses better understand their patient’s needs, putting them at ease to discuss their problems and concerns.” This further tightens the nurse and patient relationship because it allows both parties to feel emotionally relieved, and it improves the chances of the patient recovering faster. Moreover, nurses start feeling less stressed and exhausted because of the positive energy that is being transferred from their patients, a phenomenon called emotional contagion.
Giving extra care to the patients and seeing them feel more relaxed and relieved improves the mental health of nurses. Since nurses have to be on their feet for the majority of the day, seeing the patient feeling better gives positive energy to the nurses, and they feel inspired to continue working, and help the people in need. Nursing is an extremely challenging occupation that requires a lot of skills and training. To add to the fact that nurses put their life on the line, nurses also have to face challenges such as being exhausted and developing a lot of stress; however, these challenges can be overcome by their thriving motivation, and their ability to consult and comfort patients. By expressing intrinsic, integrated, and identified motivation, nurses are capable of staying on their feet all day and helping their patients. This further makes them feel more inspired to comfort and consult their patients which leads to a faster recovery. Nurses are the heroes of modern-day society because of their ability to save countless lives every single day.
Works Cited
Clark, Maria. “Importance of Patient Comfort: Benefits Go Both Ways.” Etactics, Etactics | Revenue Cycle Software, 14 Apr. 2021, https://etactics.com/blog/importance-of-patient-comfort. Accessed 17 Oct. 2021.
Galletta, Maura, et al. “A Cross‐lagged Analysis of the Relationships Among Workgroup Commitment, Motivation and Proactive Work Behaviour in Nurses.” Journal of Nursing Management, vol. 27, no. 6, Wiley Subscription Services, Inc, 2019, pp. 1148–58, doi:10.1111/jonm.12786. Accessed 17 Oct. 2021.
Lagasse, Jeff. “Healthcare Workers Experiencing Burnout, Stress Due to Covid-19 Pandemic.” Healthcare Finance News, https://www.healthcarefinancenews.com/news/healthcare-workers-experiencing-burnout-stress-due-covid-19-pandemic. Accessed 16 Oct. 2021.
“Nurse Burnout: Risks, Causes, and Precautions.” University of St. Augustine for Health Sciences, 9 Sept. 2021, https://www.usa.edu/blog/nurse-burnout/. Accessed 16 Oct. 2021.
Starc, Jasmina. “Stress Factors among Nurses at the Primary and Secondary Level of Public Sector Health Care: The Case of Slovenia.” Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, Republic of Macedonia, 10 Feb. 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5839460/. Accessed 16 Oct. 2021.
“Strategies for Managing Nurse Stress in the Workplace: Duquesne University.” Duquesne University School of Nursing, 8 Feb. 2021, https://onlinenursing.duq.edu/blog/managing-nurse-stress/. Accessed 15 Oct. 2021
“What Is a General Nurse?” What Is a General Nurse?, https://www.ecpi.edu/blog/what-is-a-general-nurse. Accessed 17 Oct. 2021.